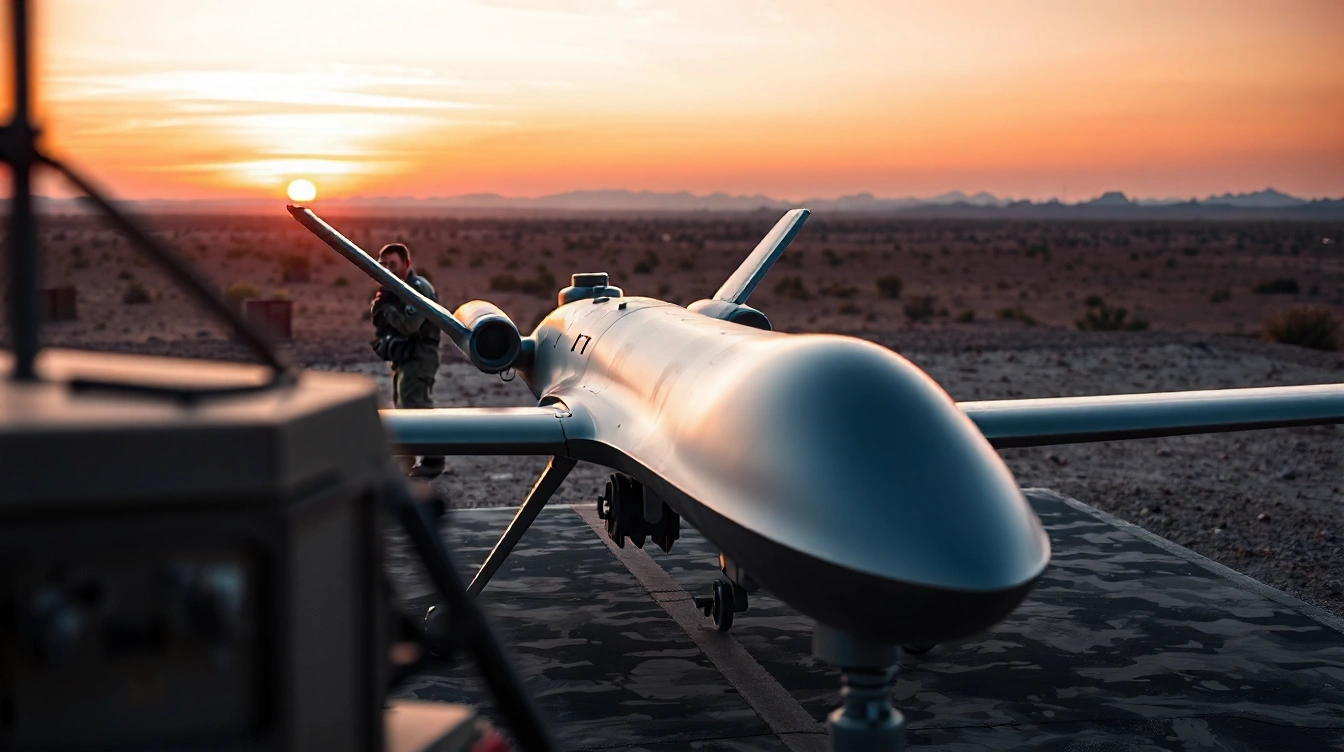
The rise of military surveillance drones has revolutionized how nations approach both security and modern warfare. These advanced systems, technically referred to as unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), extend far beyond the reach of conventional aircraft. Their quiet operation and persistent presence give armed forces a decisive edge for intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance (ISR/ISTAR) missions.
From safeguarding borders to tracking activities deep within hostile zones, these UAVs deliver vital data to commanders with remarkable speed. What distinguishes them is their rapidly evolving drone capabilities, especially new payloads and sensors that make military surveillance more accurate and comprehensive than ever before.
Have you seen this : Maximize Your Performance: Essential NVMe SSD Configuration Tips for ASUS TUF Gaming X570-Plus
The evolution of military surveillance drones
Over the last three decades, armed forces worldwide have sought increasingly sophisticated ways to conduct ISR/ISTAR. The shift from piloted reconnaissance planes to autonomous operations has fundamentally changed how conflicts are observed and targets acquired.
Modern military surveillance now relies on UAV platforms engineered for extended missions. By eliminating the need for onboard pilots, these systems allow for deep penetration into high-risk or denied areas without exposing personnel to danger. For more in-depth information, see https://elistair.com/military-surveillance-drones/
Core functions and advantages of UAVs in defense
Integrating UAVs into current defense frameworks unlocks a range of possibilities that go well beyond what traditional assets can achieve. Surveillance drones increase operational flexibility while reducing human risk during dangerous assignments.
Their greatest value lies in supporting complex tasks such as real-time monitoring, enabling leaders to track troop movements, detect enemy maneuvers, or identify terrain changes—all with minimal visibility to adversaries.
Expanding reconnaissance capabilities
Advancements in payloads and sensors have dramatically increased the scale at which UAVs collect information. With multi-spectral cameras, radar systems, and electronic signal interception, powerful ISR tools are now housed in compact drone platforms.
Operators can quickly monitor large regions, identifying suspicious activity or threats early. In joint missions, drone reconnaissance provides actionable intelligence that feeds directly into mission planning, ensuring timely and informed decisions.
Improved target acquisition and discrimination
State-of-the-art imaging technology enables UAVs to distinguish valid targets even in cluttered or camouflaged environments. Thermal imaging, laser rangefinders, and synthetic aperture radar provide precise identification, helping minimize unintended damage during subsequent actions.
This suite of technologies enhances effective target acquisition by clearly separating military objectives from civilian sites. As combat environments become more urban, the accuracy delivered by surveillance drones becomes even more critical for defense and security.
Payloads and sensors powering modern military UAVs
The effectiveness of a military surveillance drone depends heavily on its integrated payloads and sensors. While high-resolution cameras often attract attention, sensor suites also include equipment for electronic warfare, atmospheric analysis, and detection of chemical, nuclear, or biological threats.
Choosing the right combination of payloads determines how each mission unfolds. Modular drone designs allow quick adaptation, letting operators switch between sensor types for day and night reconnaissance or to support communication jamming.
- Infrared cameras for night-time surveillance
- Synthetic aperture radars for through-weather imaging
- Laser designators supporting precision strikes
- Signal intercept receivers for communication intelligence
- Real-time video streaming for live situational awareness
Rugged construction remains essential since UAVs must function reliably despite temperature extremes, vibration, and electromagnetic interference that could affect performance. High-endurance batteries or lightweight engines ensure longer missions over sensitive areas.
Gimbaled mounts and software-controlled stabilization keep advanced sensors steady, producing crisp imagery at various altitudes and speeds. Large-capacity storage, including secure options, supports both standard and encrypted transmission of sensitive ISR content.
Autonomous operations and future trends
Automation is transforming the role of UAVs in military surveillance and reconnaissance. Greater autonomy reduces operator workload, decreases response time, and boosts overall mission efficiency.
Navigation advances—such as onboard GPS, obstacle avoidance, and adaptive programming—let drones alter their flight paths autonomously. Some UAVs can operate in swarms, expanding coverage and dynamically sharing responsibilities.
Evolving AI-driven analytics
The integration of artificial intelligence allows surveillance drones to process massive amounts of data instantly, using automated image recognition to flag anomalies or potential targets. This greatly accelerates the transition from raw data to actionable intelligence.
With continued progress in machine learning, ISR/ISTAR drones are becoming better at distinguishing genuine threats amid diverse landscapes and adversary concealment tactics.
Challenges in defense and security deployment
Despite significant advances, several challenges still limit the widespread use of high-tech UAVs. Adversaries may employ electronic countermeasures to disrupt command links or sensor data streams, posing ongoing risks.
Additionally, strict regulations and complex airspace rules can restrict autonomous drone operations outside designated areas. As drone capabilities expand, continuous operator training and updated protocols remain necessary.
| ⚙️ Function | 🚁 Typical UAV system | ⏳ Operational endurance |
|---|---|---|
| Surveillance & reconnaissance | Medium-altitude long-endurance (MALE) | 24–48 hours |
| Target acquisition | Tactical mini-UAV | 1–4 hours |
| Electronic warfare | Specialized EW drone | 6–14 hours |
Frequently asked questions about military surveillance drones
What are the main roles of military surveillance drones?
- Intelligence gathering in hostile or inaccessible territories
- Target acquisition and identification before strikes
- Persistent surveillance to monitor troop activities or border security
- Electronic signals interception for communications intelligence
Which payloads and sensors are commonly used in these UAVs?
- Electro-optical/infrared cameras
- Synthetic aperture radar (SAR)
- Laser rangefinders/designators
- Weather and atmospheric sensors
- Signals intelligence packages
How do military UAVs contribute to defense and security?
| Force multiplier benefit | Contribution |
|---|---|
| Extended surveillance | Round-the-clock real-time monitoring |
| Personnel safety | No need to send crews into hostile areas |
| Intelligence integration | Data fused with other ISR sources instantly |
What challenges limit current adoption of drone capabilities in military surveillance?
- Airspace restrictions for UAV flights
- Adversary counter-drone measures
- Cost considerations for advanced sensor suites
- Rapid technological advancements requiring continuous training